Computational Statistical & Biological Physics
Prof. Dr. Felix Höfling
How are macroscopic processes in complex materials determined by their nano-scale properties? Such materials include soft, active, and biological matter and porous media. Examples of our research are
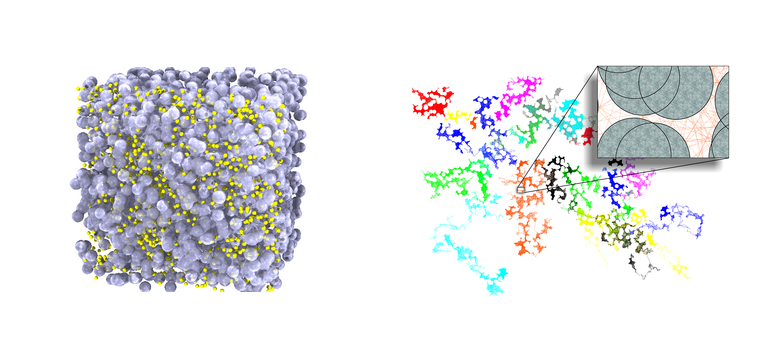
- the diffusion of proteins within cells and, more generally, in heterogeneous media,
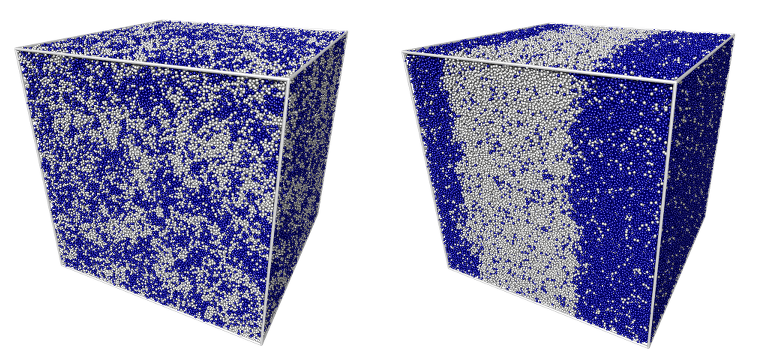
- the behaviour of water-oil mixtures at interfaces, which has potential applications in nanofluidics, and
- the spontaneous organisation of ant trails by means of communication via pheromones.
High-performance computer simulations of stochastic particle models provide us with insight into the physical mechanisms that connect the behaviour across many time and length scales. The results allow us to
- perform high precision tests of analytical predictions,
- develop new numerical methods for the data analysis,
- stimulate advancements of experimental techniques, and
- potentially discover novel physical phenomena.
Come to Berlin for a free tutorial on HAL’s MD package!
For details, drop a line at Contact.
The following examples are slightly out of date, ongoing research projects can be found at Funding.
Keywords
- critical phenomena
- high-performance computing
- intracellular transport
- liquids
- memory
- molecular dynamics
- random geometries
- reaction kinetics
- statistical mechanics
- stochastic differential equations
- stochastic particle models